A cross platform app is essential for small businesses aiming to reach a broader audience. By utilizing a single codebase, these companies ensure that your app runs smoothly on various platforms, such as iOS and Android. This approach not only saves time but also reduces costs, making it a smart choice for businesses with limited resources.
Ultimately, considering a cross platform app development guarantees a consistent user experience across all devices. This uniformity enhances brand recognition and user satisfaction, crucial elements for any business looking to build a loyal customer base. Moreover, the streamlined development process allows for quicker updates and easier maintenance. As easy as the whole cross platform app development may sound, it is surely much more complex.
This is why Deftsoft has come up with a detailed blog post on cross platform app development – allowing you to facilitate this process smoothly. This blog post discusses the key benefits, reliable tools/frameworks, and platforms supported by cross-platform app development. Since cross platform app development is a multifaceted practice, we’ll also dig deep into its application uses across various industries. In the end, you’ll get to know comprehensively about the challenges and emerging trends in this innovative development.
So, don’t wait now! Without further, jump into this blog post to read.
What is Cross Platform App Development?
Cross platform app development refers to the process of creating mobile applications that can run on multiple operating systems, such as iOS and Android, from a single codebase. This approach utilizes tools and frameworks like Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin to streamline the development process.
Benefits of Cross Platform App Development
The key advantages of cross platform app development include cost savings, faster time-to-market, and a consistent user experience across different devices. These benefits make it an ideal choice for small businesses looking to maximize their impact with minimal investment. Let’s discuss each in detail!
1. Cost-Effectiveness
Cross platform app development services offer significant cost savings for small businesses. By developing a single codebase that runs on multiple platforms, businesses can reduce the need for multiple development teams. This consolidation leads to lower overall development expenses.
Furthermore, maintaining one codebase is more economical than managing separate versions for each platform. Updates and bug fixes can be implemented once and deployed across all platforms, reducing ongoing maintenance costs and ensuring a more streamlined development process.
2. Time Efficiency:
Cross platform app development enable faster time-to-market by allowing simultaneous deployment on multiple platforms. This speed is crucial for businesses looking to launch their products quickly and gain a competitive edge.
The development process is also more efficient, as developers can focus on optimizing one codebase instead of juggling multiple ones. This streamlined approach accelerates the development cycle, ensuring that businesses can respond rapidly to market demands and user feedback.
3. Consistency:
Using cross platform app development ensures a consistent user experience across different devices and platforms. This uniformity helps in building a solid brand identity, as users encounter the same interface and functionality regardless of their device. Consistency across platforms also enhances user satisfaction, as it minimizes the learning curve and potential frustrations with different app versions. This seamless experience is vital for retaining customers and encouraging positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
What are the Core Technologies/Frameworks Used for Cross Platform App Development
Cross platform app development relies on several core technologies to create applications that run seamlessly on multiple platforms. These technologies provide the foundation for building robust, high-performance apps that meet diverse business needs. Let’s explore some of the most popular and powerful frameworks used in this domain:
1. Flutter
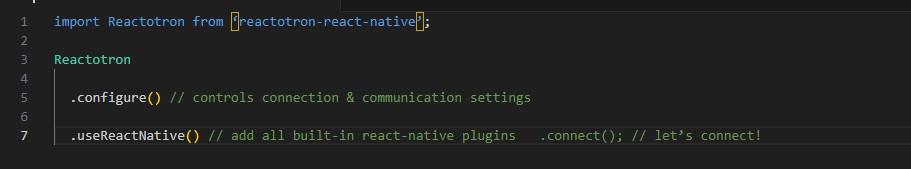
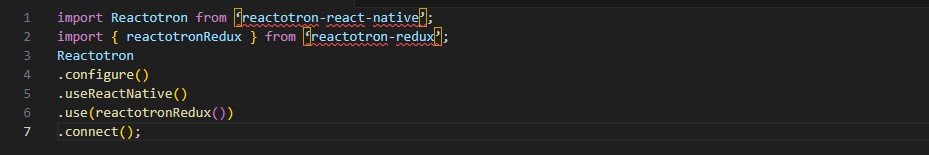
Flutter, developed by Google, is a leading technology in the realm of cross platform app development. It uses the Dart programming language and offers a comprehensive set of pre-designed widgets. These widgets enable developers to create highly responsive and visually appealing user interfaces. Flutter’s hot reload feature allows developers to see changes in real time, significantly speeding up the development process. Its rich set of libraries and tools makes it an ideal choice for creating high-quality mobile apps that perform consistently across both iOS and Android platforms.
2. React Native
React Native, created by Facebook, is another prominent framework used in cross platform app development. It allows developers to use JavaScript and React to build mobile applications. One of the key advantages of React Native is its ability to leverage native components, which ensures a high level of performance and a native-like user experience. React Native also has a large and active community, providing a wealth of resources, plugins, and tools that make development more efficient and effective.
3. Xamarin
Owned by Microsoft, Xamarin uses C# and .NET to provide a robust environment for cross platform development. Xamarin allows developers to write most of their code once and share it across multiple platforms, including iOS, Android, and Windows. This not only accelerates the development process but also ensures a consistent user experience across different devices. Xamarin’s integration with Visual Studio, a powerful IDE, further enhances the development workflow, making it easier to build, test, and deploy cross platform applications.
Also read: 8 Leading Cross Development Frameworks
What are the Platforms Supported by Cross Platform App Development?
Cross platform app development services are designed to create applications that work seamlessly across a wide range of platforms. This broad compatibility ensures that businesses can reach a larger audience without the need for separate native apps for each platform. The key platforms supported include:

1. iOS
Cross-platform development tools like Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin make it easier to build iOS apps that run smoothly across devices. These tools provide access to native iOS features and functionalities, ensuring the apps deliver a high-quality user experience while adhering to Apple’s strict guidelines.
2. Android
Android is another major platform supported by cross platform development tools. These tools allow developers to create apps that work efficiently on a wide range of Android devices, from smartphones to tablets. The ability to reach a large and diverse user base makes Android support essential for any cross platform app.
3. Windows
Cross platform app development also extends to Windows, allowing businesses to create applications that run on Windows PCs and tablets. This capability is particularly useful for enterprise applications that need to support a range of devices used in corporate environments.
4. macOS
In addition to iOS, cross platform tools also support macOS, enabling the development of desktop applications for Apple’s operating system. This ensures that businesses can provide a consistent experience across both mobile and desktop platforms.
5. Web
Many cross platform development tools also support the creation of web applications. This allows businesses to reach users on any device with a web browser, providing maximum flexibility and accessibility. Web support is crucial for creating progressive web apps (PWAs) that deliver a native-like experience on the web.
Cross Platform Development Tools
The success of cross platform Development depends on a robust set of development tools and frameworks that streamline the development process and enhance productivity. Some of the key tools used in this field include:
1. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs):
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) are essential for cross platform development. Visual Studio, Android Studio, and Xcode are among the most popular IDEs used by developers. Visual Studio, with its powerful debugging and coding tools, is widely used for Xamarin development. Android Studio provides a comprehensive environment for building Android apps, while Xcode is the go-to IDE for macOS and iOS development. These IDEs offer a range of features that facilitate coding, testing, and deployment, making the development process more efficient.
2. Build Tools:
Build tools like Gradle and Maven are crucial for managing dependencies and automating the build process. Gradle is widely used in Android app development, providing a flexible and efficient way to manage project builds. Maven, often used in conjunction with Java projects, helps manage project dependencies and build lifecycle, ensuring that the app is built and deployed correctly.
3. Testing Frameworks:
Testing is a critical component of cross platform app development, ensuring that the app functions correctly on all supported platforms. Appium and XCTest are popular testing frameworks used in this domain. Appium is an open-source tool that allows automated testing of mobile applications, supporting both iOS and Android platforms. XCTest, developed by Apple, is used to test iOS applications, providing a robust set of tools for unit and UI testing.
By leveraging these core technologies, platforms, and tools, cross platform development services enable businesses to create high-quality, versatile applications that meet the needs of a diverse user base. This approach not only enhances development efficiency but also ensures a consistent and engaging user experience across all devices.
Applications of Cross Platform App Development (Industry-Wise)
Cross platform app development has become a game-changer across numerous industries by providing a unified approach to app creation that works across different operating systems. This versatility is highly valued in various sectors:
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, cross platform apps streamline patient management, appointment scheduling, and telemedicine services. By utilizing a single codebase, healthcare providers can ensure that their apps offer consistent functionality and user experience across both iOS and Android devices. This efficiency supports better patient engagement and more effective management of medical records.
- Retail: Retail businesses leverage cross platform development to create shopping apps that enhance the customer experience with features like product catalogs, real-time inventory updates, and secure payment gateways. These apps help retailers maintain a strong digital presence, reaching a wider audience without the need for separate development efforts for different platforms.
- Finance: Financial institutions benefit from cross platform apps by offering banking services, investment tracking, and personal finance management tools across various devices. This approach ensures that users can access their financial information securely and consistently, regardless of the device they use.
- Education: Educational institutions use cross platform apps to deliver e-learning platforms, interactive courses, and student management systems. These apps provide a seamless educational experience for students and educators, making learning accessible from different devices and operating systems.
- Travel and Hospitality: The travel industry utilizes cross platform app development for booking systems, travel itineraries, and customer support. This consistency across devices enhances the user experience, allowing travelers to manage their trips effortlessly, whether they’re using smartphones or tablets.
Cross platform development provides a flexible, cost-effective solution for industries seeking to reach diverse audiences while maintaining a high-quality user experience.
Challenges and Limitations in Cross Platform Development
Cross platform app development has become an attractive option for businesses looking to reach a wider audience with a single codebase. However, despite the advantages, cross platform development comes with its own set of challenges and limitations that can affect the final product’s quality and user experience. Below, we’ll explore some of the key challenges and limitations in cross platform development.
1. Performance Issues
One of the most significant challenges in cross platform app development is performance. While cross platform frameworks have made strides in optimizing performance, they often cannot match the performance of native apps. Native apps are built specifically for a particular operating system, allowing them to leverage the platform’s full capabilities, including advanced graphics and hardware acceleration.
In contrast, cross platform apps may struggle with performance, particularly in areas like graphics rendering and animations. This is because cross platform frameworks rely on a layer of abstraction that communicates with the underlying native code, leading to potential delays and lag. For performance-intensive applications, such as those involving complex animations, gaming, or augmented reality (AR), these issues can significantly impact the user experience. Users may notice slower load times, frame drops, or less responsive interactions, all of which can detract from the app’s overall usability and appeal.
2. Limited Access to Native Features
Another limitation of cross platform development is the restricted access to native features and APIs. While cross platform app development frameworks offer a broad range of functionalities, they may not fully support all the native features available on each platform. This limitation can hinder the development of apps that require deep integration with the device’s hardware or operating system-specific features.
For example, if an app needs to utilize the latest camera technology, biometric authentication, or advanced geolocation services, cross platform frameworks may not offer the same level of access or performance as native development. In some cases, developers may need to write custom native code to bridge the gap, which can complicate the development process and reduce the advantages of using a cross platform approach. Additionally, the delay in updates and support for new native features can leave cross platform apps lagging behind their native counterparts.
3. Potentially Higher Initial Costs
While one of the primary benefits of cross platform development is the potential for cost savings, especially when maintaining and updating apps across multiple platforms, the initial investment can be higher than anticipated. This is particularly true for small businesses or startups with limited resources.
The learning curve associated with new cross platform frameworks can be steep, requiring developers to familiarise themselves with the specific tools, libraries, and best practices of the chosen framework. Additionally, setting up the development environment and ensuring that the app works seamlessly across different devices and operating systems can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
These initial costs, both in terms of time and money, may outweigh the long-term benefits for some businesses. It’s essential to carefully assess whether the potential savings in maintenance and updates justify the upfront investment. In some cases, especially for simple or small-scale apps, native development might offer a more straightforward and cost-effective solution.
Emerging Trends in Cross Platform Development in 2025
Cross platform development has rapidly evolved, with new trends and technologies reshaping the landscape. As businesses increasingly seek to deliver apps across multiple platforms with minimal effort, developers are continually innovating to improve performance, user experience, and development efficiency. Below are three emerging trends in cross platform development that are gaining traction.
1. Hybrid Frameworks Combining Native and Web Technologies
A growing trend is the use of hybrid frameworks that blend native and web technologies to create more versatile and high-performing apps. Frameworks like Ionic and React Native enable developers to use web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript while still allowing access to native features through plugins or custom modules. This approach offers the flexibility of web development with the performance and functionality of native apps, making it an attractive option for developers looking to balance ease of development with high-quality user experiences.
2. Adoption of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are gaining popularity as an alternative to traditional cross platform apps. PWAs offer a seamless user experience by combining the best features of web and mobile apps, including offline access, push notifications, and the ability to install on the home screen without requiring app store downloads. PWAs are built using standard web technologies, making them easier to develop and maintain. They also provide a more consistent experience across different devices and operating systems, making them an appealing choice for businesses looking to reach a wide audience without the complexities of native app development.
3. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into cross platform development is an emerging trend that enhances app functionality and user experience. Cross platform app frameworks are increasingly supporting AI and ML capabilities, allowing developers to build intelligent features like personalized recommendations, voice recognition, and predictive analytics directly into their apps. This trend is particularly important as businesses seek to create more interactive and intuitive apps that can adapt to user behavior. As AI and ML technologies continue to advance, their role in cross platform development is expected to grow, enabling more sophisticated and responsive applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cross platform app development is becoming increasingly vital for businesses aiming to maximize their reach and efficiency. As emerging trends such as hybrid frameworks, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), and AI integration reshape the development landscape, companies can now create more versatile, high-performing apps with minimal effort. These innovations not only streamline the development process but also enhance user experience across various platforms. While challenges like performance issues and limited access to native features persist, the evolving tools and technologies are making cross platform development more accessible and effective. By staying ahead of these trends, businesses can leverage the full potential of cross platform development to create robust, user-friendly applications that meet diverse market needs.
If you’re in need of a reliable partner for cross platform app development, look no further than Deftsoft. With 19+ years of experience, we have established ourselves as a premier source for top-tier cross platform app development services. Our expert team specializes in creating seamless, high-performance applications that run flawlessly across multiple platforms, including iOS, Android, and Windows. Trust Deftsoft to deliver innovative solutions that save you time and money while expanding your reach. Partner with us today and experience the difference of working with a top cross platform app development company.
FAQs
1. What is cross-platform app development?
Cross-platform app development refers to creating mobile applications that can run on multiple operating systems, like iOS and Android, using a single codebase. This approach saves time and resources by allowing developers to write one set of code that works across different platforms.
2. What are the advantages of cross-platform app development?
The main advantages include reduced development costs, faster time to market, and broader audience reach. Additionally, maintaining a single codebase simplifies updates and bug fixes across all platforms.
3. Which frameworks are popular for cross-platform app development?
Popular frameworks include Flutter, React Native, Xamarin, and Unity. Each offers unique features that make it easier to build high-quality apps that perform well across different platforms.
4. How does cross-platform app development impact app performance?
Modern cross-platform tools have significantly improved performance, allowing apps to run smoothly with near-native functionality. However, for highly complex apps, native development might still offer better performance.
5. Is cross-platform app development suitable for all types of apps?
Cross-platform development is ideal for most business apps, e-commerce solutions, and social platforms. However, for apps requiring extensive platform-specific functionalities, like high-end gaming or complex AR/VR applications, native development may be more appropriate.