A technology that started with a digital currency called Bitcoin has now opened the door to building fully functional apps. Many people confuse Ethereum with Bitcoin; however, they’re not the same.
If you’re intrigued by the idea of creating a decentralized app (dApp) on the Ethereum blockchain platform, then this guide is a treasure trove of knowledge for you. It’s your key to unlocking the world of dApp development. Let’s get started.
Is Ethereum Just Another Bitcoin?
Ethereum is not a digital currency like Bitcoin. However, it is a software platform built on blockchain that allows developers to build decentralized apps (dApps).
Ethereum was ideated by Russian-Canadian programmer and cryptocurrency researcher Vitalic Bitterin in 2013. Later, in 2015, it went live. The simplest explanation of Ethereum in two words is ‘Software platform.’
So, how does Ethereum differ from Bitcoin?
“Bitcoin and Ethereum are both use cases of blockchain technology with different purposes.”
– CryptoCasey’s podcast
Bitcoin is simply a digital currency that people can use as a form of payment to send to and from each other or hold as a store of value. On the other hand, Ethereum is a programmable blockchain that people can use to build software to create valuable products and services due to the decentralization properties of blockchain technology.
The software that people can build on Ethereum is called decentralized applications or dApps.
What Exactly is a dApp?
A decentralized app or dApp is an app whose data is stored on a distributed network of computers. It is a Web3 app that can be developed on a platform that is built on blockchain. A dApp enjoys three main benefits of being developed on a blockchain network. These are:
- Decentralization
The blockchain network is decentralized. Firstly, it means that the data is stored on a group of computers (nodes) rather than on a central server. Secondly, the network is not owned by any third-party intermediary, not even the government.
- Transparency
Another important asset of blockchain is transparency. This means that the transactions recorded on the ledger are available for everyone to see and are stored on a network of computers around the world, thus making data impossible to alter or modify.
- Immutability
Immutability simply means that the data recorded and stored on the blockchain cannot be changed, altered or forged. This un-modification of records is achieved through cryptography and blockchain hashing processes.
In simple words, when a Web3 developer builds a dApp on a blockchain network like Ethereum, he knows that no one can control the data or network or destroy it.
Also Read: The Beginner’s Handbook to Decentralized Apps (dApps)
Things to Know Before Building a dApp on Ethereum
There are two main things to know before beginning to build a dApp on Ethereum. Follow along!
- Know About Gas Fee
As discussed before, blockchain is decentralized, meaning it is software distributed across a vast network of computers around the world to incentivize people to host and maintain data on the blockchain. Ether was created as a form of payment to fuel the Ethereum network.
So, anyone who wants to build a software application, i.e., dApp on an Ethereum network has to pay for the computing power and space required for using Ether. The amount of Ether required for network fees is determined by a built-in pricing system known as Gas.
Note: You only need to pay the gas fee for dApp deployment.
- Proficient in JavaScript and/or Solidity
If you’re entirely new to blockchain and dApp development, you cannot directly jump on learning about blockchain programming languages. You must first have the time and patience to learn a basic programming language such as JavaScript or Python. You must also be aware of front-end development as well. It is only then that you can plunge your hands into blockchain programming languages such as Solidity or Go to build smart contracts from dApp.
How to Create a dApp on Ethereum Step-by-Step?
Now that you’re aware of what you need to create a dApp on Ethereum let’s address our primary focus: how to build a dApp on Ethereum. There are numerous steps involved in building a dApp, such as setting up the development environment to deploy the smart contract and then creating a frontend so that the users can interact with the app.
Follow the given roadmap to build dApp on Ethereum:
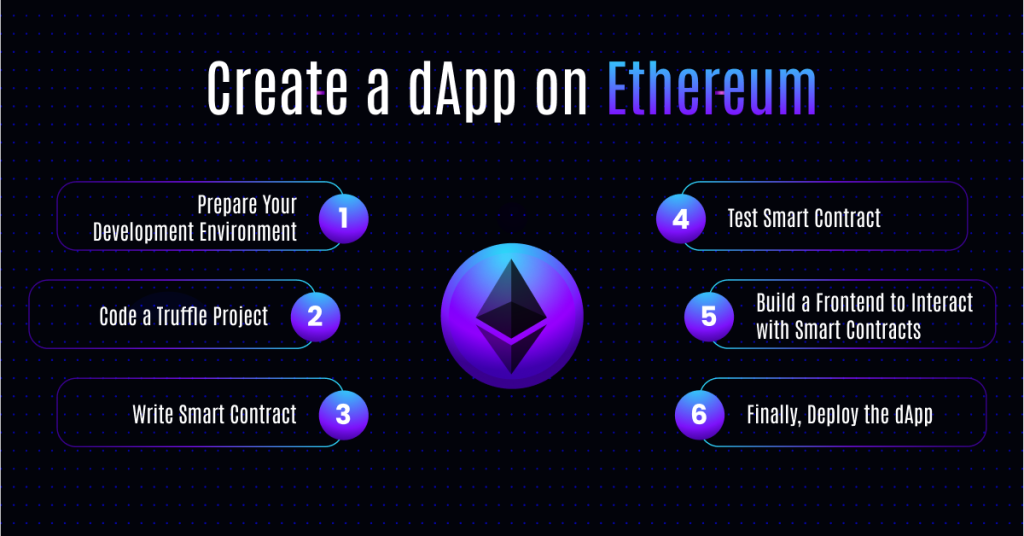
1. Prepare Your Development Environment
You need to install the following tools and runtime environment:
- Install Node.js runtime environment and npm package to run JavaScript applications and manage packages. You can download Node.js from here.
- The next step is to download Truffle, a popular development framework for Ethereum. You can install Truffle with the following bash script on Node.js:
npm install -g truffle
- Then, download Ganache, an Ethereum development tool that allows you to simulate the blockchain environment locally and deploy smart contracts.
- It is important to download a software cryptocurrency wallet to interact with Ethereum. To do this, download MetaMask, a browser extension for managing Ethereum accounts and interacting with the blockchain.
2. Code a Truffle Project
After installing all the required tools, create a new Truffle project and set up your directory infrastructure. The goal of Truffle is to deploy dApps and smart contracts to Ethereum. It offers you all the tools and libraries to simplify development, building the contract, testing, deploying and managing it.
3. Write Smart Contract
You can write the smart contract in Solidity, which is one of the most widely used blockchain programming languages for Ethereum. Compile and migrate the smart contract using Truffle. A good tip is to connect your GitHub repository to Truffle Teams.
4. Test Smart Contract
You can write the tests in Mocha and Chai to test the functioning of your smart contract.
5. Build a Frontend to Interact with Smart Contracts
To interact with the smart contract, you need a front-end framework such as React.js. This allows you to integrate Web3.js with the Ethereum blockchain.
6. Finally, Deploy the dApp
Once you’re satisfied with the created version of your dApp, it’s time to deploy your smart contract to Ethereum. You can promote it to production by deploying it to Mainnet or any testnet. After that, connect your frontend with the deployed contract.
Build a dApp on Ethereum with an Example
It’s good to have practical knowledge, but what’s fun when you don’t know how to code the dApp in real life? To make it easy, we’ve taken an example of a peer-to-peer lending dApp that you can build by following these steps. Consider this practice as a warmup exercise so that you can get started with creating your own dApp on Ethereum.
Here are the practical steps to build a dApp on Ethereum:
- Set Up Development Environment
The steps are already mentioned above.
- Creating a Truffle Project
- Use the following bash script to initialize the Truffle project:
mkdir LendingDApp
cd LendingDApp
truffle init
- Use the following Arduino code to prepare the directory structure:
LendingDApp/
├── contracts/
│ ├── Migrations.sol
│ └── Lending.sol
├── migrations/
│ ├── 1_initial_migration.js
│ └── 2_deploy_contracts.js
├── test/
├── truffle-config.js
- Write the Smart Contract
- Create ‘Lending.sol’ in ‘contracts’ folder by writing the following Solidity code:
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Lending {
struct Loan {
uint256 amount;
address payable borrower;
address payable lender;
uint256 interest;
bool repaid;
}
Loan[] public loans;
mapping(address => uint256[]) public borrowerLoans;
mapping(address => uint256[]) public lenderLoans;
event LoanRequested(uint256 loanId, address borrower, uint256 amount, uint256 interest);
event LoanFunded(uint256 loanId, address lender);
event LoanRepaid(uint256 loanId);
function requestLoan(uint256 amount, uint256 interest) external {
loans.push(Loan({
amount: amount,
borrower: payable(msg.sender),
lender: payable(address(0)),
interest: interest,
repaid: false
}));
uint256 loanId = loans.length – 1;
borrowerLoans[msg.sender].push(loanId);
emit LoanRequested(loanId, msg.sender, amount, interest);
}
function fundLoan(uint256 loanId) external payable {
Loan storage loan = loans[loanId];
require(loan.lender == address(0), “Loan already funded”);
require(msg.value == loan.amount, “Incorrect amount”);
loan.lender = payable(msg.sender);
lenderLoans[msg.sender].push(loanId);
loan.borrower.transfer(loan.amount);
emit LoanFunded(loanId, msg.sender);
}
function repayLoan(uint256 loanId) external payable {
Loan storage loan = loans[loanId];
require(msg.sender == loan.borrower, “Only borrower can repay”);
require(!loan.repaid, “Loan already repaid”);
uint256 repaymentAmount = loan.amount + loan.interest;
require(msg.value == repaymentAmount, “Incorrect repayment amount”);
loan.repaid = true;
loan.lender.transfer(repaymentAmount);
emit LoanRepaid(loanId);
}
function getLoanDetails(uint256 loanId) external view returns (uint256, address, address, uint256, bool) {
Loan storage loan = loans[loanId];
return (loan.amount, loan.borrower, loan.lender, loan.interest, loan.repaid);
}
}
- Compile the smart contract through the following bash script:
truffle compile
- Create ‘2_deploy_contracts.js’ in ‘migrations’ folder using the following JavaScript code:
const Lending = artifacts.require(“Lending”);
module.exports = function (deployer) {
deployer.deploy(Lending);
};
- Migrate the Smart Contract
You the following bash script to migrate the smart contract:
truffle migrate
- Test the Smart Contract
- Create ‘Lending.test.js’ in ‘test’ folder by writing the JavaScript code:
const Lending = artifacts.require(“Lending”);
contract(“Lending”, accounts => {
it(“should allow a user to request a loan”, async () => {
const instance = await Lending.deployed();
await instance.requestLoan(100, 10, { from: accounts[0] });
const loan = await instance.loans.call(0);
assert.equal(loan.amount, 100, “Loan amount should be 100”);
assert.equal(loan.interest, 10, “Loan interest should be 10”);
assert.equal(loan.borrower, accounts[0], “Borrower should be the account requesting the loan”);
assert.equal(loan.lender, 0x0, “Lender should be empty initially”);
});
it(“should allow a user to fund a loan”, async () => {
const instance = await Lending.deployed();
await instance.fundLoan(0, { from: accounts[1], value: 100 });
const loan = await instance.loans.call(0);
assert.equal(loan.lender, accounts[1], “Lender should be the account funding the loan”);
});
it(“should allow a borrower to repay a loan”, async () => {
const instance = await Lending.deployed();
await instance.repayLoan(0, { from: accounts[0], value: 110 });
const loan = await instance.loans.call(0);
assert.equal(loan.repaid, true, “Loan should be marked as repaid”);
});
});
- Run the test by using the bash script:
truffle test
- Build the Frontend to Interact with Smart Contracts
- Set up the React app by using the following bash script:
npx create-react-app lending-dapp
cd lending-dapp
- You then need to install Web3.js through the following bash script:
npm install web3
- Create App.js components by using the following JavaScript code:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from ‘react’;
import Web3 from ‘web3’;
import Lending from ‘./contracts/Lending.json’;
const App = () => {
const [web3, setWeb3] = useState(null);
const [account, setAccount] = useState(null);
const [contract, setContract] = useState(null);
const [loans, setLoans] = useState([]);
const [loanAmount, setLoanAmount] = useState(“”);
const [loanInterest, setLoanInterest] = useState(“”);
useEffect(() => {
const init = async () => {
const web3 = new Web3(Web3.givenProvider || ‘http://localhost:7545’);
const accounts = await web3.eth.requestAccounts();
const networkId = await web3.eth.net.getId();
const deployedNetwork = Lending.networks[networkId];
const instance = new web3.eth.Contract(
Lending.abi,
deployedNetwork && deployedNetwork.address,
);
const loanCount = await instance.methods.loansCount().call();
const loanDetails = [];
for (let i = 0; i < loanCount; i++) {
const loan = await instance.methods.getLoanDetails(i).call();
loanDetails.push(loan);
}
setWeb3(web3);
setAccount(accounts[0]);
setContract(instance);
setLoans(loanDetails);
};
init();
}, []);
const requestLoan = async () => {
await contract.methods.requestLoan(loanAmount, loanInterest).send({ from: account });
setLoanAmount(“”);
setLoanInterest(“”);
};
const fundLoan = async (loanId, amount) => {
await contract.methods.fundLoan(loanId).send({ from: account, value: amount });
};
const repayLoan = async (loanId, amount) => {
await contract.methods.repayLoan(loanId).send({ from: account, value: amount });
};
if (!web3 || !contract) {
return <div>Loading Web3, accounts, and contract…</div>;
}
return (
<div className=”App”>
<h1>P2P Lending DApp</h1>
<h2>Request a Loan</h2>
<input
type=”number”
value={loanAmount}
onChange={e => setLoanAmount(e.target.value)}
placeholder=”Loan Amount”
/>
<input
type=”number”
value={loanInterest}
onChange={e => setLoanInterest(e.target.value)}
placeholder=”Loan Interest”
/>
<button onClick={requestLoan}>Request Loan</button>
<h2>Loans</h2>
<ul>
{loans.map((loan, index) => (
<li key={index}>
Amount: {loan[0]} – Interest: {loan[3]} – Borrower: {loan[1]} – Lender: {loan[2]} – Repaid: {loan[4].toString()}
{!loan[4] && (
<>
<button onClick={() => fundLoan(index, loan[0])}>Fund Loan</button>
<button onClick={() => repayLoan(index, parseInt(loan[0]) + parseInt(loan[3]))}>Repay Loan</button>
</>
)}
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
- Connect with smart contract:
Make sure that your frontend is connected to the right network where your smart contract is deployed.
- Deploy the dApp
After testing the dApp, the final step is to deploy the smart contract to Ethereum Testnet or Mainnet. Leverage the following steps to do so:
- Update ‘truffle-config.js’ with the suitable network configuration (e.g., Rinkeby, Mainnet). You can deploy using Truffle through the following bash code:
truffle migrate –network <network-name>
- Deploy the Frontend
You can then use a hosting service such as GitHub Pages, Netlify or Vercel to host your React app.
Conclusion
That’s a wrap! If you’re a mere beginner or intermediate and want to refer to a guide on how to build a dApp on Ethereum, this blog is the perfect guide to get started. You can follow the complete roadmap to create your dApp. All you need to do is set up a development environment for creating a smart contract and then test and deploy the dApp.
If you’re an enterprise or business organization looking to build dApps, Deftsoft has a dedicated team of seasoned dApp developers who can build a professional dApp for your business venture. We’re here to help.
FAQs:
1. What is the first step in building a dApp on Ethereum?
The first step in building a dApp on Ethereum is to prepare your development environment. This includes installing Node.js, npm, Truffle, Ganache, and MetaMask. These tools are essential for running JavaScript applications, managing packages, simulating the blockchain environment locally, and managing Ethereum accounts.
2. Do I need to know any specific programming languages to create a dApp on Ethereum?
Yes, to create a dApp on Ethereum, you should be proficient in JavaScript and have a good understanding of front-end development. Additionally, you will need to learn Solidity, the programming language used for writing smart contracts on Ethereum.
3. What is the role of Gas fees in building a dApp on Ethereum?
Gas fees are required for deploying and running transactions on the Ethereum network. When you build a dApp on Ethereum, you need to pay these fees in Ether (ETH) to compensate for the computing power and storage space utilized on the network.
4. How do I test my smart contract during the dApp development process?
You can test your smart contract by writing tests using Mocha and Chai frameworks. These tests help ensure that your smart contract functions correctly before deploying it to the Ethereum network. Truffle provides built-in support for these testing frameworks.
5. What are the main benefits of developing a dApp on the Ethereum blockchain?
The main benefits of developing a dApp on the Ethereum blockchain include decentralization, transparency, and immutability. Decentralization ensures that the data is stored on multiple nodes rather than a central server. Transparency allows anyone to view the transactions recorded on the blockchain. Immutability means that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted.