
Move to AEM Cloud Service Like a Pro: Step-by-Step Guide
-
By Shamsher Singh Bhullar
-
13th February 2024
Is there a world where a CMS does not need any maintenance? Yes, there is! The stakes went high in 2020 when Adobe Experience Manager introduced AEM as a cloud service in January. AEM has been a pioneer in migrating on-premise software to the cloud since the beginning. Having said that, AEM cloud service is no surprise.
This state-of-the-art content management system is AEM’s cloud-native solution. Enterprises and business organizations can bring their most ambitious customer experiences to life. It transcends the conventional content management and delivery standards and redefines digital content and campaign personalization.
This blog is the exact beginner-friendly guide to migrating Adobe Experience Manager Sites, Assets, and Managed Services to the cloud. Before discussing, we will also navigate through what AEM as a cloud service is, what the benefits of the AEM cloud service are, and what’s new in AEM cloud service.
What’s AEM Cloud Service? How is It Different from the Traditional AEM?
AEM as a Cloud Service is one of the most revolutionary offerings by Adobe Experience Manager. It is specially formulated to build customized, personalized, optimized, and content-led experiences. With extraordinary power through its sophisticated scalability, Agile methodology, and flexibility, it has become the preferred choice of service for top-notch enterprises.
Since everything is hosted on the cloud, enterprises can say goodbye to the massive number of software updates, downtime experienced due to scheduled maintenance cycles, and scalability issues.

To sum up, AEM as a cloud service renders the following dollar-worthy features that are worth your every penny:
- Always-ON:
The AEM cloud service never faces downtime. Since all the maintenance tasks are handled in the backend by the AEM itself, enterprises can harness the mighty features of AEM as a cloud service.
- Always Up-to-Date:
The AEM cloud service does not require manual refreshes or a human workforce to check software updates. It always stays updated to the latest versions.
- Always at a Perfect Scale:
Since the AEM cloud offers auto-scalability features, enterprises can save capital and deploy their budget to create customer segmentation and content personalization. This cloud-native solution scales up and down when required without human intervention.
- Performance Resiliency:
The AEM as a cloud service is unique since it focuses on curating a seamless, robust, and efficient digital and content solution for enterprises. It caters to users with resilient performance through its high speed.
- Secure by Default:
The AEM cloud provides secure solutions proactively. It looks for vulnerabilities in the software and, thus, offers quick fixes for the identified set of errors, bugs, and weaknesses. This feature allows enterprises to invest in other significant resources.
- Intelligent Microservices:
AEM cloud service also offers various intelligent microservices. For example, a highly performant asset ingestion service integrates Adobe Sensei with the latest research technologies like smart tagging, cropping, etc.
The above highlighting features make it different from the traditional Adobe Experience Manager services that do not offer such robust features.
How Do You Migrate to AEM as a Cloud Service?
The primary goal of AEM cloud service is to eliminate the load of planning for product updates and instead focus on innovating novel ideas for elevated enterprise success. After all, AEM as a cloud service is a secure, scalable, flexible, and extendible solution for digital marketers and IT professionals.
One can boost their website and digital asset performance efficiencies by moving to the AEM cloud services. The AEM cloud takes responsibility for automatically rolling out new product features by testing and optimizing the features on the backend. This phenomenon ensures that the enterprise teams get the best and state-of-the-art applications.
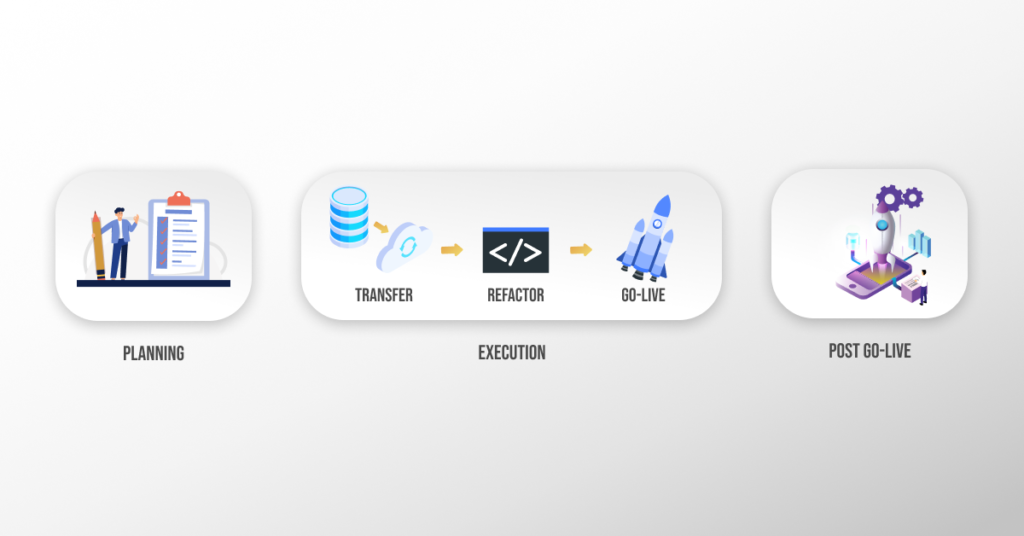
There are three main phases of moving to AEM cloud service. These are mentioned as follows:
- Planning
- Execution
- Post Go-live
These phases can be illustrated in a high-level form as the following:
1. Planning:
Before you plunge into the practice of migrating to AEM cloud service, you must check your readiness to assess these AEM cloud services. You can do so by running tests through the Best Practices Analyzer (BPA) on the source environment.

After running tests, it is a pivotal practice to establish project Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), define success criteria, and fix project timeframes.
2. Executing:
The next step is execution. It involves the process of deploying project code to an Experience Manager Cloud service instance. To implement this practically, one must thoroughly educate oneself about the AEM Cloud Manager.
With the help of Cloud Manager, enterprises can manage the AEM as a cloud service quickly and seamlessly. It has dedicated Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) frameworks. These frameworks speed up the process of customized deliveries and updates without degrading the performance.
The next steps involved in the execution stage are mentioned as follows:
A. Content Migration
In the execution process, the first step is to migrate all the content from the existing AEM instance to the AEM cloud service instance. It can be done using the following two tools:
- Content Transfer Tool:
This tool is used to transfer content from an on-premise or AMS Adobe Experience Manager instance to an AEM cloud service instance.
- Package Manager:
It is a zip file that is used to import and export mutable content of the repository.
B. Refactor/Optimize Existing Code
You must first compile your code using the SDK API Jar and review AEM Dev guidelines, such as log running jobs and background tasks, sling schedulers, input stream usage, etc.
The code restructuring process without changing the code’s external behavior entails the code refactoring process. Code refactoring aims to ensure that the existing code is compatible with AEM as a cloud service.
The code refactoring process includes the following:
- Running Best Practices Analyzer (BPA) on the source environment.
- Considering project structuring based on Cloud Archetype.
- Separating the code from the content, i.e., mutable and immutable. For instance, /apps and /libs are considered immutable; however,/content, /conf, /var, /etc, /oak:index, /system, /tmp, etc. are mutable, which means that they can be changed anytime during the runtime.
- Reviewing and executing the required changes in the code and deploying them on a local SDK.
- Performing smoke testing with the help of AEM SDK.
The Repository Modernizer tool is one of the best tools to modify multiple AEM Maven projects to a compatible version for AEM as a cloud service. You can follow the below demonstrated Maven project structure to perform code refactoring:
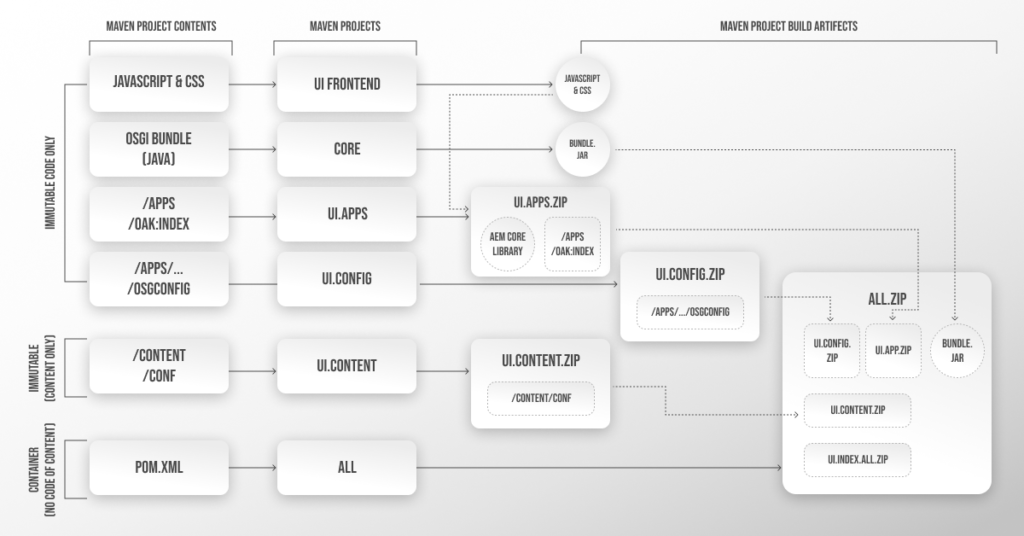
You can speed up the code refactoring process using tools such as Dispatcher Converter, Asset Workflow Migration, and the AEM Modernizer tool. You can review Dispatcher configurations for refactoring.

C. Deployment/Go Live:
Now that you’ve executed the code, it is time to deploy it. AEM provides its own single git repository, which uses Cloud Manager’s CI/CD pipelines to deploy the code. If you don’t want to use AEM’s repo, you can also use an on-premise or customer-managed git repo with AEM Cloud Manager.
You can then run the customer code through the Cloud Manager Quality pipeline.
It is important to test the code after deploying it. You can perform test cycles using various types of tests such as smoke testing, QA, and many more. After validating the test, your AEM instance is ready to go live on the AEM Cloud Service.
3. Post Go-Live:
After going live, cleaning up temporary files, managing logs, and ensuring you’re following the best industry practices are crucial. It is important to make sure that everything is working as expected after going live.
Do You Really Need to Ditch Your Current CMS for AEM Cloud Service?
AEM Cloud Service is indeed a hefty investment, especially if you’re an enterprise already deploying an efficient CMS. In such a case, do you really need to shift to AEM cloud service?
You can either ask your CMS or cross-check yourself to find if your answers are positive for the following questions:
- Does your CMS scale up and down automatically in times of abrupt increase in traffic flow?
- Is your CMS solution 99.99% available?
- Does your CMS fix bugs and update software automatically at its backend?
If your answer is affirmative to the above questions, you don’t need to upgrade. However, if it was negative even for two pointers, it is time to switch to Adobe AEM as a cloud service.
It’s a Wrap!
That’s all for the guide for AEM as a cloud service local setup. The world is abruptly adopting the power of cloud computing, and the digital world is at the apex of the line. An enterprise can supercharge its productivity and efficiency by seamlessly following this migration guide to AEM cloud service.
If you’re looking for a detailed step-by-step guide to moving from AEM to AEM cloud service, this is the perfect guide for you. We mentioned the three most pivotal phases of the migration process, how to tackle emerging issues, and whatnot.
Stay tuned for more AEM-related guides and updates with Deftsoft!
FAQs:
What is meant by AEM cloud services?
AEM as a cloud service is a new-generation solution to working in scalable, highly available, and Agile environments. It is a cloud-native solution for all the AEM instances, such as Adobe Experience Manager Assets, Adobe Experience Manager Sites, AEM Managed Services, etc. It also offers new software updates and keeps the AEM instances up-to-date. Therefore, it reduces pressure on IT teams and marketers so that they can focus on other productive tasks.
What is required to access AEM as a cloud service?
An enterprise user must be added to a group of the required Cloud Service Products. There are various AEM Administrators and AEM user profiles. You also need to make sure that your AEM instances are compatible with the recent releases of the latest version of the AEM cloud service.
What tools are used for migrating to AEM as a cloud service?
There are mainly two tools that are used for migrating to AEM as a cloud service. These are: 1. Content Transfer Tool, 2. Package Manager.
What is the key difference between Adobe Managed Service (AMS) and AEM as a cloud service (AEMasCS)?
Adobe Managed Service is a hosting offering by Adobe Experience Manager for the conventional AEM 6.5. On the other hand, AEM as a cloud service is a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offering by Adobe that provides scalability, high availability, elasticity, security, and agility for varied AEM instances.
What is the difference between AEM 6.5 and AEM cloud service?
Since AEM as a cloud service is a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), i.e., it is not hosted locally on a data center. Therefore, it is lighter than the traditional Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) 6.5. Also, AEM cloud service has a lower ownership cost than AEM.
Recent Articles
-

Unity vs Unreal Engine 5: Which is Better?
-

Non-Negotiable Tips for Developing a P2P Lending Platform
-
The 8 Leading Cross-Platform App Development Frameworks You Should Know
-

Step-by-Step Guide: How to Build a dApp on Ethereum with Ease
-

Why Does Your Business Need Blockchain Development Company’s Expertise?

Shamsher Singh Bhullar
 13th February 2024
13th February 2024