How are Public Blockchains Different from Private Blockchains?
-
By Paramjit Singh
-
2nd November 2023
Hey there, fellow blockchain enthusiast! Ever wondered if the technology powering Bitcoin and NFTs is a one-size-fits-all deal? You know, like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole? Well, you’re in good company because, just like choosing between streaming platforms for your next binge-watch session, deciding between public and private blockchains can be a bit of a head-scratcher, too. As a blockchain explorer, you must choose between public and private blockchains. (Doesn’t sound like something from a Sci-Fi Action movie?)
Remember in “The Matrix’ when Neo had to choose between the red pill and the blue pill? Well, consider this scene in your life, too. The only difference is instead of pills, there are public and private blockchains. Each holds its own unique powers and purposes, much like Neo’s choice to embrace the unknown or stick to the familiar.
But you don’t have to worry about anything; our blog post will act as your trusted guide to help you understand the key differences between private and public blockchain so that you can decide which option fits your business. Before exploring the key differences, it would be great to discuss public and private blockchains independently. So, let’s roll in!
What is a Public Blockchain?

Many people question what is a public blockchain since many of them interlink it with Bitcoin or cryptocurrency exclusively.
So, here is the correct answer to this question.
A public blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that has open networks, allowing anyone to participate in it. It means public blockchain is non-restrictive and permissionless. This also serves as one of the main differences between private and public blockchain. They rely on a consensus mechanism, typically Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), to validate transactions.
Key Features of Public Blockchains:
- Decentralization:
Public blockchains are maintained by a global network of nodes, each participating in transaction validation and block creation. This feature plays one of the differences between private and public blockchains. The decentralized nature of public blockchains eliminates the need for intermediaries.
- Permissionless Access:
Anyone can participate in a public blockchain network. Users can create wallets, make transactions, and even contribute to the network’s consensus mechanism.
- Transparency and Immutability:
All transactions on a public blockchain are recorded on an open ledger, visible to anyone. Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring transparency and trust. This is one of the primary differences between private and public blockchains.
Examples of Public Blockchains:
- Bitcoin: Pioneered by Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin introduced the concept of cryptocurrency and remains the most well-known public blockchain. It primarily serves as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system.
- Ethereum: Ethereum revolutionized blockchain technology by introducing smart contracts, enabling the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
- Binance Smart Chain (BSC): BSC is a parallel blockchain to Binance Chain, designed to support smart contracts and DApps. It offers compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and boasts high transaction throughput.
Use Cases for Public Blockchains:
- Cryptocurrency Transactions: Public blockchains like Bitcoin serve as a medium of exchange for digital assets, allowing secure and transparent peer-to-peer transactions.
- Smart Contracts: Ethereum’s smart contract functionality enables the execution of self-executing contracts with predefined conditions without the need for intermediaries.
- Decentralized Applications (DApps): Public blockchains provide a foundation for building decentralized applications that operate autonomously without a central authority. Moreover, this also serves as one of the differences between private and public blockchains.
Advantages of Public Blockchains:
- Accessibility: Public blockchains are open to anyone with an internet connection, fostering inclusivity and global participation.
- Security through Consensus Mechanisms: The consensus mechanisms employed in public blockchains ensure that malicious actors cannot easily compromise the network. Moreover, fundraising methods like IEO, STO and ICO also benefits from public blockchain’s mechanism.
- Network Effect: Public blockchains benefit from a large and diverse user base, creating a robust ecosystem of developers, miners, and users. This also acts as one of the primary differences between private and public blockchains.
What is a Private Blockchain?

Unlike public blockchains, Private blockchains are centralized networks where access and control are restricted to a specific group of participants. This is the main difference between private and public blockchain. Permissioned access is granted to entities known as validators who authenticate transactions. Enhanced privacy and control are central to the design of private blockchains.
Key Features of Private Blockchains:
- Centralization: Private blockchains are controlled by a predefined set of validators or participants. This centralization allows for greater control over the network.
- Permissioned Access: Access to a private blockchain is restricted to authorized participants, typically selected by the network’s administrator or governing entity. This is one of the key differences between private and public blockchain.
- Enhanced Privacy: Private blockchains often implement encryption and privacy features to restrict access to sensitive information, making them suitable for enterprise applications.
Examples of Private Blockchains:
- Hyperledger Fabric: Developed by the Linux Foundation, Hyperledger Fabric is a permissioned blockchain framework designed for enterprise solutions. It provides a modular architecture and supports smart contracts.
- Corda: Corda is an open-source blockchain platform tailored for businesses. It facilitates secure and private transactions between parties while ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Quorum: Developed by JPMorgan Chase, Quorum is an enterprise-focused blockchain platform based on Ethereum. It emphasizes privacy and confidentiality in financial transactions.
Use Cases for Private Blockchains:
- Enterprise Solutions: Private blockchains are well-suited for businesses seeking to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance transparency within a controlled environment.
- Supply Chain Management: They are employed to track and verify the provenance of goods, ensuring authenticity and compliance with industry standards.
- Government Applications: Private blockchains are utilized in government systems to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency in areas such as identity management and voting. This acts as one of the main differences between private and public blockchains.
Advantages of Private Blockchains:
- Enhanced Privacy and Control: Private blockchains offer a level of confidentiality and control over data that may be critical for sensitive enterprise applications.
- Scalability for Specific Use Cases: Since the number of participants is limited and known in advance, private blockchains can achieve higher transaction speeds and scalability for specific business needs. This also acts as one of the main differences between private and public blockchains.
- Compliance with Regulations: Private blockchains can be tailored to meet regulatory requirements, making them an attractive option for industries with strict compliance standards.
Comparing Public and Private Blockchains:
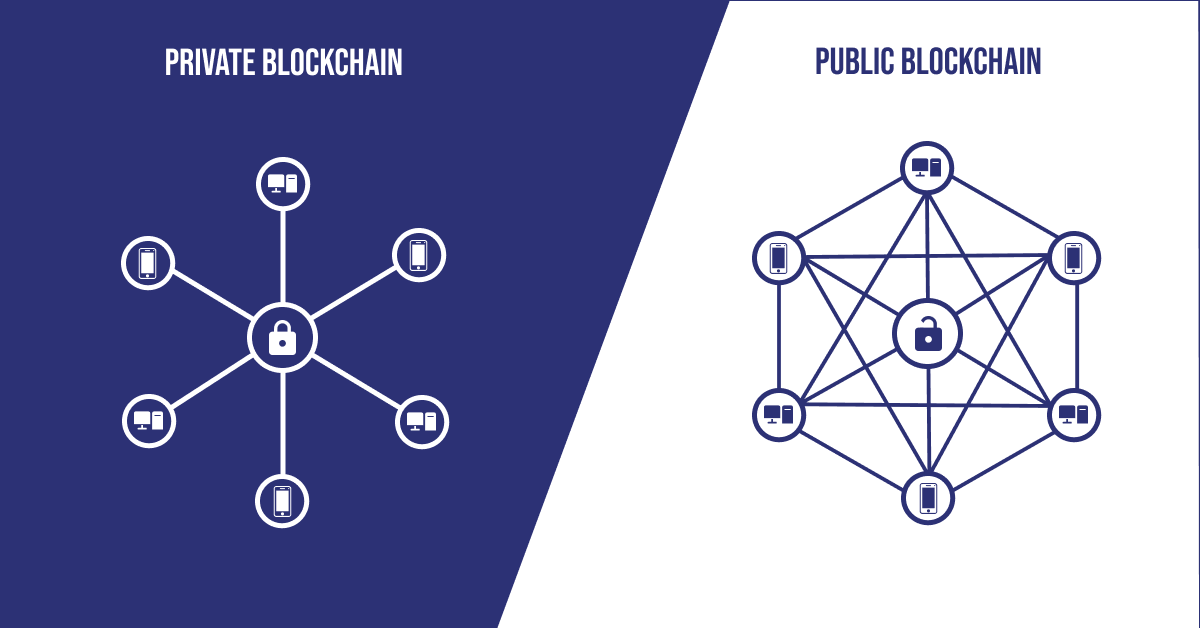
The differences between private and public blockchain extend to various critical aspects, including governance, consensus mechanisms, security models, performance, and use case suitability. These factors play a crucial role in determining which type of blockchain is best suited for a particular application. Let’s start with private vs public blockchain.
1. Governance and Access Control:
- Public Blockchains: Governed by a decentralized network of nodes with open access for all.
- Private Blockchains: Governed by a centralized entity with restricted access to authorized participants.
2. Consensus Mechanisms:
- Public Blockchains: Often employ energy-intensive mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or more energy-efficient methods like Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Private Blockchains: Utilize consensus mechanisms tailored to the specific needs of the network, such as Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) or Raft.
3. Blockchain Key (Public and Private Keys in Blockchain):
- Public Blockchains: Visible on the blockchain and serve as the destination for receiving funds. Anyone can see these addresses and send transactions to them.
- Private Blockchains: Access is restricted to a specific group of participants. These participants are typically known and trusted entities. Each participant has a set of keys for authentication.
4. Security and Trust Models:
- Public Blockchains: Rely on the collective computational power of nodes to secure the network, ensuring resistance against attacks.
- Private Blockchains: Place trust in a predefined set of validators, providing a controlled environment with lower computational requirements.
5. Performance and Scalability:
- Public Blockchains: May face scalability challenges due to the high number of participants and the need for consensus among them.
- Private Blockchains: This can achieve higher transaction speeds and scalability since the number of participants is limited and known.
6. Use Case Suitability:
- Public Blockchains: Ideal for applications requiring transparency, decentralization, and a large user base, such as cryptocurrency transactions and decentralized applications. This also serves as one of the differences between private and public blockchains.
- Private Blockchains: Suited for enterprise solutions, supply chain management, and government applications where privacy, control, and compliance are paramount.
Critical Considerations for Choosing Between Public and Private Blockchains:
Factors Influencing the Decision:
Let’s take a break from private blockchain vs public blockchain and discuss some top factors to consider while choosing between public and private blockchains.
- Security Requirements: Assess the level of security required for your application. If dealing with sensitive information, a private blockchain may be more suitable.
- Regulatory Compliance: Consider whether your industry or application requires compliance with specific regulations. Private blockchains can be tailored to meet regulatory standards.
- Use Case Specifics: Evaluate the specific requirements of your use case, including the need for transparency, the number of participants, and the level of control required.
Use Case Examples and Recommendations:
- Supply Chain Management: If your use case involves tracking the provenance of goods in a complex supply chain, a private blockchain may be the preferred choice due to enhanced privacy and control.
- Cryptocurrency Transactions: For a peer-to-peer digital cash system, a public blockchain like Bitcoin would be a natural choice, as it relies on a decentralized network for security.
- Enterprise Solutions: Private blockchains are well-suited for businesses looking to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance transparency within a controlled environment.
Future Trends in Blockchain Technology:
1. Interoperability Between Public and Private Blockchains:
As the blockchain space evolves, we can expect increased interoperability between public and private blockchains. This will enable seamless data transfer and operations between different types of blockchain networks. Ultimately, the differences between private and public blockchain will also get narrower.
2. Cross-Chain Communication:
Efforts to facilitate cross-chain communication are on the rise. Solutions like blockchain bridges and protocols that allow different blockchains to communicate and transact with each other will become more prevalent. In this way, the differences between private and public blockchains will be shortened.
3. Evolution of Consensus Mechanisms:
Consensus mechanisms will continue to evolve, with a focus on energy efficiency, scalability, and security. New models may emerge to address the limitations of current mechanisms.
Deftsoft: A Trusted Savior for Blockchain-related Problems
Deftsoft emerges as the trusted savior for all your blockchain-related challenges. With an experience of 17 years of delivering innovative blockchain solutions, Deftsoft offers expertise that goes beyond conventional development. Whether it’s creating secure applications (public blockchains or implementing smart contracts, we lead the way. Our client-centric approach and commitment to excellence make us the go-to partner for navigating the complexities of blockchain technology. After understanding the differences between private and public blockchains, what may your final decision be? Deftsoft will help you develop a secure application that fits your needs.
Final Thoughts:
In the dynamic landscape of blockchain technology, the choice between public and private blockchains is a critical decision that shapes the trajectory of your project. With a clear understanding of the differences between private and public blockchain, you can navigate the blockchain landscape with confidence. But, to develop a blockchain, you may require years of experience, advanced techniques, skills, and resources. And many of you wouldn’t even have this. So, consider Deftsoft’s blockchain development services to achieve your requirements. Whether you choose a public or private blockchain, Deftsoft stands as a trusted partner, offering 17 years of expertise in crafting innovative blockchain solutions. With a client-centric approach, we are committed to helping you navigate the complexities of blockchain technology and develop secure applications tailored to your needs. Embrace the future of blockchain with Deftsoft by your side.
FAQs:
- What is the difference between private and public blockchain?
A public blockchain is not controlled by any individual or group of individuals. Anyone can make use of the public block. For example, Bitcoin is a decentralized blockchain digital asset that can be used by anyone for online transactions. On the other hand, a private blockchain is a centralized network owned by a group of people. You need access to private blockchain transactions.
- What are the types of blockchain?
There are four main types of blockchain: public blockchain, private blockchain, consortium blockchain, and hybrid blockchain.
- Why is private blockchain faster than public blockchain?
The transactional speed of private blockchain is more because it is centralized only a few authorities have access to the network. Public blockchain networks are decentralized because of which the blocks take time to be created. This is why public blockchains are relatively slower.
- What is an example of private blockchain?
Hyperledger Fabric, R3 Corda, Quorum, and Ethereum Enterprise are some examples of private blockchain. These are mostly blockchain frameworks or blockchain protocols.
- Are Bitcoin and Ethereum private blockchains?
Both Bitcoin and Ethereum are public blockchains since they are decentralized. Anyone can join as a node (computer) on the network of these public blockchains and verify transactions.
- Can someone hack a blockchain?
No, a blockchain cannot be hacked. However, if some malicious code is added to the chain with brute force, blockchain assets can be stolen. Blockchain transactions can also be altered.
- Where are private blockchain used?
Private Blockchains are used in large-scale banks such as JPMorgan and Citi to secure transactions without compromising the transaction speed.
- What are the features of blockchain?
The main features of blockchain are decentralization, top-notch security, immutability, and distributed ledger. These features make blockchain technology reliable, fast, secure, and efficient.
Recent Articles
-

Unity vs Unreal Engine 5: Which is Better?
-

Non-Negotiable Tips for Developing a P2P Lending Platform
-
The 8 Leading Cross-Platform App Development Frameworks You Should Know
-

Step-by-Step Guide: How to Build a dApp on Ethereum with Ease
-

Why Does Your Business Need Blockchain Development Company’s Expertise?

Paramjit Singh
 2nd November 2023
2nd November 2023