Blockchain: A Revolution in Digital Trust and Transparency
-
By Paramjit Singh
-
16th September 2023
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, blockchain development has emerged as a revolutionary concept that has disrupted traditional systems of trust, transparency, and data management. The components of Blockchain have transformed industries from finance to healthcare, and its potential applications continue to expand. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the essence of blockchain, its key components, and real-world examples to understand how this technology is changing how we interact, transact, and trust in the digital age.
The Foundation of Blockchain
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers to ensure their immutability and transparency. This decentralized nature is one of its defining features and differentiates it from traditional centralized systems, such as banks or government databases.
A central authority (like a bank) holds and controls all transaction data in a traditional system. In contrast, blockchain disperses this data across a network of computers known as nodes. Each node stores a copy of the entire blockchain, and there is no single point of control. This decentralization reduces the risk of manipulation or fraud, as no single entity has full authority.
Key Components of a Blockchain
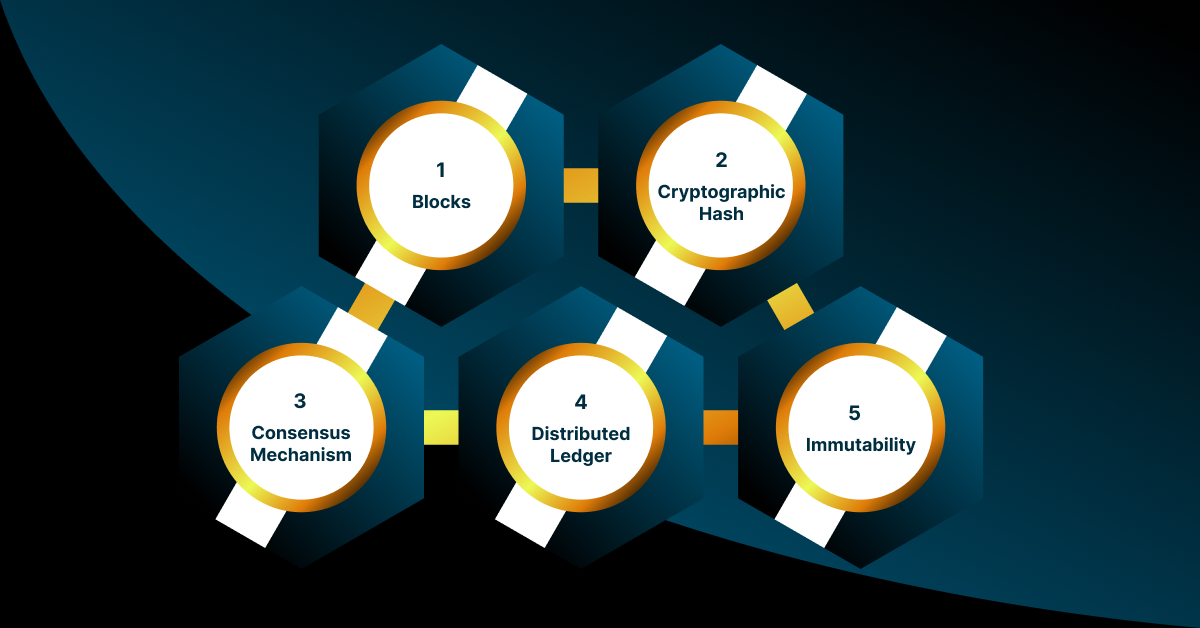 To understand how a blockchain works, it’s essential to grasp its key components and how they interact:
To understand how a blockchain works, it’s essential to grasp its key components and how they interact:
1. Blocks: A blockchain is a chain of blocks, each containing a set of transactions. These transactions can represent anything from financial transfers to asset ownership records. Blocks are linked together in chronological order, forming a chain.
2. Cryptographic Hash: Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, which creates a secure and immutable connection between them. If the data in a block is altered, the hash changes, indicating tampering.
3. Consensus Mechanism: For transactions to be added to the components of the blockchain, there must be a consensus among the nodes in the network. Common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). PoW requires nodes to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions, while PoS relies on a node’s cryptocurrency.
4. Distributed Ledger: All nodes in the network have a copy of the ledger, ensuring transparency. Once a transaction is validated, it is added to all copies of the catalog simultaneously.
5. Immutability: Once a block is added to the chain, its contents are immutable and cannot be altered without the consensus of most nodes. This immutability enhances trust in the system.
How Blockchain Works: An Example
Let’s explore how a blockchain works with a simple example: Alice wants to send digital currency to Bob using a blockchain-based system.
Step 1: Alice initiates a transaction, creating a digital record of her intent to send a certain amount of cryptocurrency to Bob.
Step 2: This transaction is broadcast to the blockchain network, where nodes validate its authenticity and accuracy using the consensus mechanism.
Step 3: Once the transaction is verified, it is bundled with other transactions into a block. The block includes a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure link.
Step 4: Miners, responsible for validating and adding transactions to the blockchain, compete to solve a complex mathematical problem. The first miner to solve it gets to add a new block to the chain. This process is resource-intensive and is a central feature of PoW-based blockchains like Bitcoin.
Step 5: Once the block is added, all nodes will update copies of the ledger to reflect the new transaction. The catalog is now updated and transparent, with the transaction visible to anyone on the network.
Step 6: The transaction is considered secure and immutable, as altering it would require changing all copies of the ledger across the network, which is computationally infeasible.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain

Blockchain development extends far beyond cryptocurrencies. It has found applications in various industries addressing trust, transparency, and security challenges. Here are some notable examples:
1. Finance: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have revolutionized digital payments and introduced decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, allowing users to borrow, lend, and trade digital assets without intermediaries.
2. Supply Chain Management: Companies like IBM and Walmart use blockchain to track product origins, enhancing transparency and traceability. This is particularly valuable in industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where knowing the source of products is critical.
3. Healthcare: Medical records and drug supply chains in the healthcare industry can greatly benefit from Blockchain in Healthcare Industry, thanks to its unparalleled security and transparency. With blockchain technology, patients gain greater control over their health data, while healthcare providers can confidently ensure data integrity and privacy.
4. Voting Systems: Blockchain can enhance the security and integrity of electronic voting systems by creating a tamper-proof ledger of votes cast, preventing fraud and manipulation.
5. Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts automatically enforce and facilitate the terms of agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries in various sectors, from insurance to real estate.
6. Energy Trading: Blockchain enables peer-to-peer energy trading, directly allowing individuals and businesses to buy and sell excess renewable energy, promoting sustainability and efficiency.
Challenges and Future Potential
While the components of blockchain offers significant advantages, it also faces challenges. Scalability, energy consumption (particularly in PoW systems), and regulatory hurdles are among the concerns that must be addressed.
However, the potential of blockchain technology is immense. As it matures and evolves, it can reshape industries, streamline processes, and enhance trust in the digital world. With ongoing research and development, blockchain’s role in society is poised to grow, bringing about new opportunities and possibilities we have yet to imagine.
Bottom Line
Blockchain development is a transformative technology that has revolutionized how we trust and transact in the digital age. Its decentralized and transparent nature and cryptographic security have enabled various applications across industries. As blockchain continues to evolve and address its challenges, its impact on our society will likely deepen, offering innovative solutions to longstanding problems and redefining how we conduct business and interact in the digital world. For those looking to harness the full potential of blockchain technology, Deftsoft’s reliable blockchain development services is the answer. Our team of expert blockchain developers unlock new opportunities and harness the benefits of this ground-breaking innovation. So, what are you waiting for? Contact us today to enjoy the top-class blockchain services.
Recent Articles
-

Unity vs Unreal Engine 5: Which is Better?
-

Non-Negotiable Tips for Developing a P2P Lending Platform
-
The 8 Leading Cross-Platform App Development Frameworks You Should Know
-

Step-by-Step Guide: How to Build a dApp on Ethereum with Ease
-

Why Does Your Business Need Blockchain Development Company’s Expertise?

Paramjit Singh
 16th September 2023
16th September 2023