Cracking the Code: How dApps Differ from Traditional Apps
-
By Paramjit Singh
-
30th January 2024
Welcome to the world of Web 3.0, where the world is dominated by Artificial Intelligence, NFTs, decentralization, and whatnot. dApps are the epitome of Web 3.0 as they mark the beginning of a new era. The global decentralized apps (dApps) market is forecasted to witness a golden era between 2024 and 2030, especially in North America.
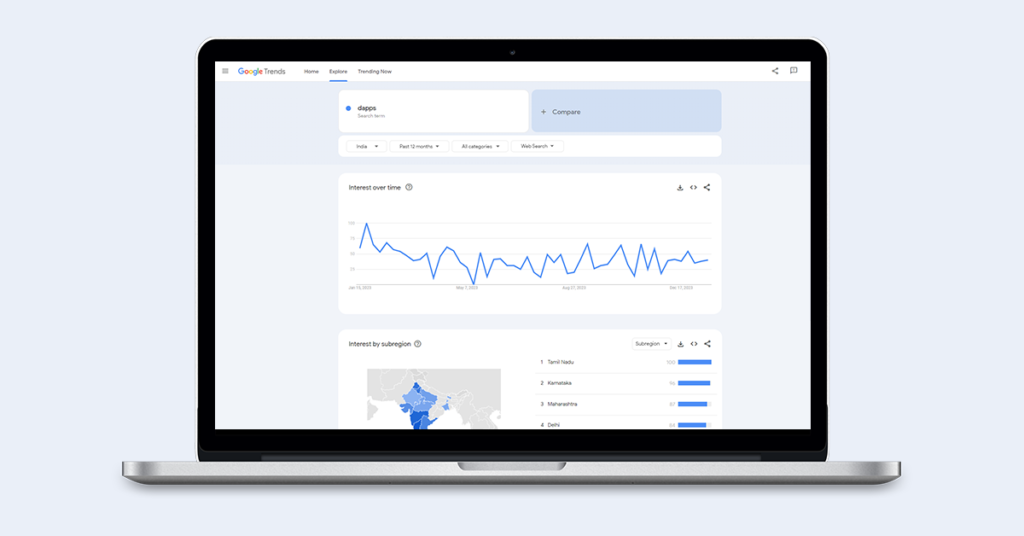
The dApp market size is expected to grow by millions by 2031 with an exponential CAGR. According to Google Trends, the interest has shot up significantly over time.
In this blog, you will learn what a dApp is, how it is different from traditional apps with the help of a real-life example, how a dApp works, and lastly, what the benefits and disadvantages of these dApps are.
Let’s delve into the unconventional world of decentralized apps.
What’s the Fuss about dApps?
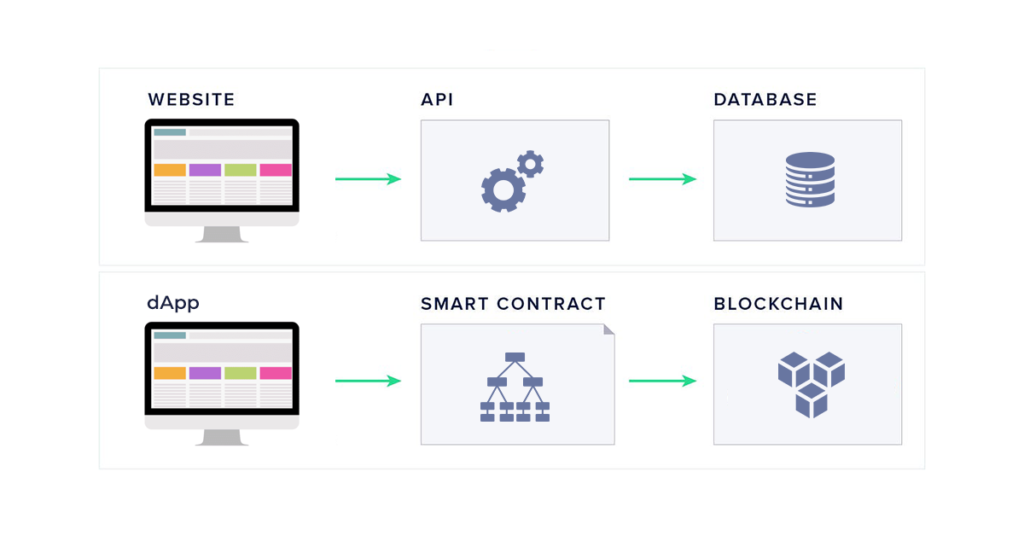
Expanded as Decentralized Applications (dApps), dApps are not controlled by any organization as they are not hosted on servers, unlike conventional mobile apps. This means that the app user can directly access these dApps through blockchain or any other kind of decentralized computing. It is an open-source software platform applicable to decentralized blockchains.
Before you begin relating the term dApps with cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, let me stop you right there! You need to know that dApps can only be built on smart contract networks. This means that Bitcoin cannot use dApps. On the other hand, Ethereum can utilize smart contracts, which are nothing but a chunk of code that comprises a program to be run by the dApps.
To sum up, dApps are made up of two major things:
- A front end to be used by a user
- A back end that either depends on the code instructed in the smart contracts or a peer-to-peer (P2P) blockchain network
How is a dApp Different from a Traditional Web 2.0 App?
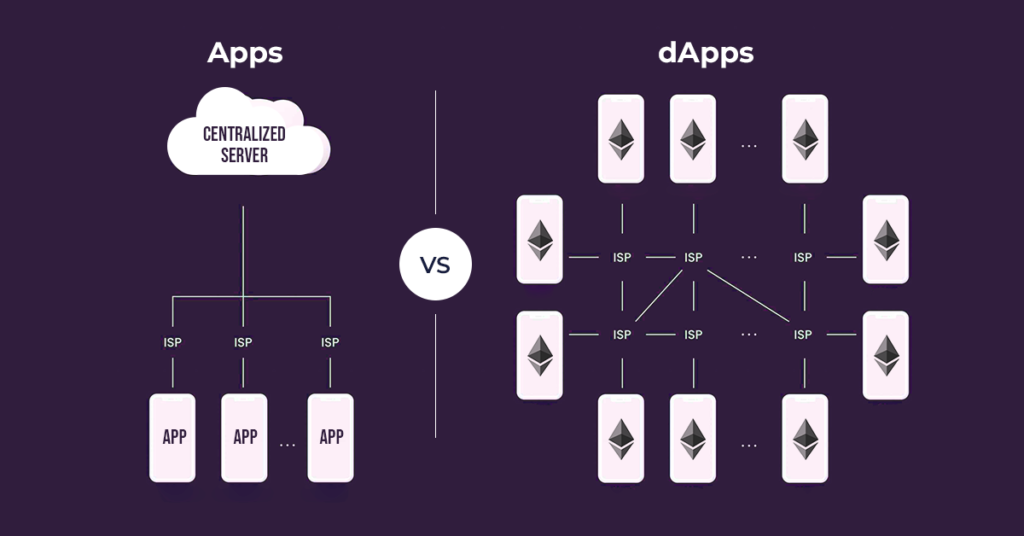
Let’s understand how a dApp differs from a traditional app by taking the example of a social media app like Instagram. The app is created by some creators and is hosted on cloud services such as Amazon Web Services (AWS). This means that a central authority is involved when a user uses the app. In fact, it can even face downtime due to some technical reasons.
dApps, on the other hand, are not under the control of any authority, do not face downtime, and they stay up and running 24/7. The best part about dApps is that you can access the source code (smart contract) by paying in cryptocurrency to the developer. Therefore, a dApp is transparent, doesn’t include any central authority, and is decentralized.
The highlighting differences between the two are evident from the below pointers:
dApps
- A dApp is not owned by any organization or individual.
- It runs on blockchain or decentralized computing.
- It can never be closed and never faces downtime.
- There is transparency in the source code in the form of the smart contract.
- A user can access a dApp by exchanging tokens.
Traditional Apps
- A traditional app has an owner and is hosted on servers.
- It runs on the Internet or the traditional Web 2.0.
- A traditional app such as Facebook can face downtime.
- A user can never crack the code of the source for a conventional Wbeb 2.0 app.
- Transactions are made through currency such as USD.
What’s a Real-Life Example of a dApp?
“Everything that can be decentralized, will be decentralized”.
“Johnston’s Law”
dApps have established their unmatched identity in various industries. We have quoted examples from real life in the gaming and financial sectors. The examples are as follows:
A Gaming dApp at a Glance
dApps is an emerging technology that is trickling down into various industries like banking and finance, gaming, social media, and online shopping. One of the best real-life examples of a dApp is Cryptokitties.

Tiny kitties can be purchased using the dApp Cryptokitties. In a technical sense, what you are purchasing is the NFT data of rights to that particular token, which stands in for that cat.
You may gather these kittens and even breed them to produce additional kittens, which is the entertaining aspect of the game. If you play the game for a long enough period of time, you can sell older-generation kittens for a profit or a loss because they are typically more valued.
Even more strangely, you can use the blockchain to rent out your kitten so that it can procreate with someone else’s kitten.
Decentralized Financial App on the Go
Many apps are designed to be used for lending and borrowing. The well-known one is AAVE.

Any user can fund specific smart contracts with ETH or MATIC tokens using the AAVE platform. You may practically invest your coins and tokens when you deposit them since you will be rewarded with an interest rate.
Additionally, if you have provided sufficient collateral, AAVE lets you borrow tokens. To cut to the chase, this lets you take out loans at various interest rates and even set up margin positions.
How does a dApp Work?
The backend code of a decentralized app runs on a peer-to-peer decentralized network. Similar to how regular apps are created, it can also have a frontend and user interface written in any language. You can host the front end on any decentralized server, such as IPFS. dApps operate similarly to traditional apps, with the following few exceptions as addressed below:
The following features of the dApp are noteworthy:
- Decentralized: A decentralized application runs on Ethereum, a public, open platform.
- Consistency: dApps operate in the same way no matter what environment they’re running in.
- Agile: Given the necessary resources, dApps can carry out any task.
- Isolated virtual environment: Decentralized applications run within the Ethereum Virtual Machine, a virtualized environment designed to prevent smart contract bugs from interfering with the regular operation of the blockchain network.
What are the Benefits of dApps?
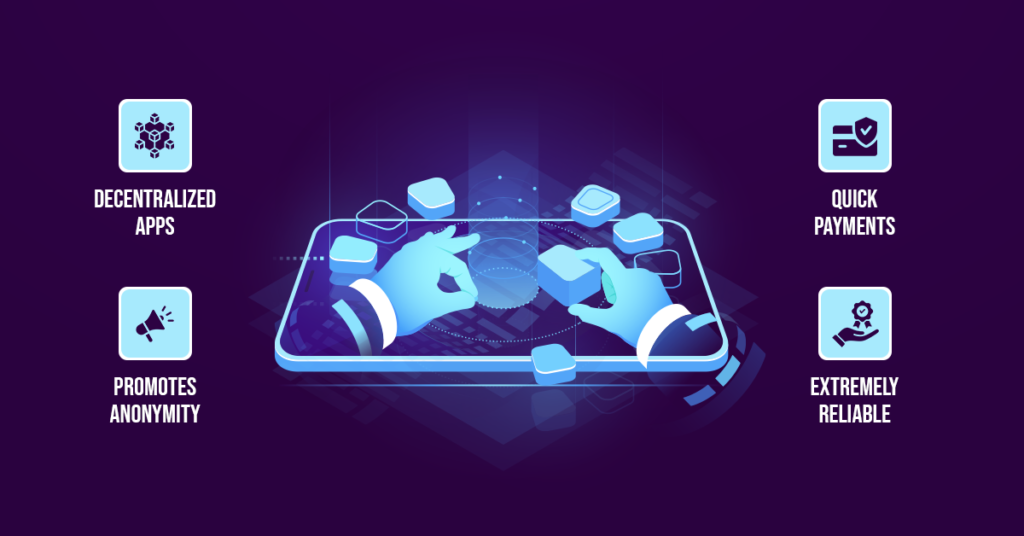

The benefits of dApps are mentioned below:
- Decentralized apps: These applications are not compromised because they are decentralized, and it is impossible to alter the records. Furthermore, be aware that they are extremely safe and do not obstruct hacking, incursion, or any other potentially harmful activity.
- Promotes anonymity: It promotes greater anonymity because these apps do not require users to follow drawn-out registration procedures.
- Quick payments: It allows the processing of instant payments because there are no intermediary apps like integrated payment gateways.
- Extremely reliable: It provides reliable data records because users can access the public blockchain to verify transaction details.
What are the Disadvantages of dApps?
Given how wonderful everything seems, why don’t more people use decentralized apps? Well, there are numerous drawbacks, thus defying it as the users’ first choice.
- Extremely high costs: The price is becoming the worst aspect of separated programs. All of it just comes at a high financial cost. It will also cost you money to maintain any information on the blockchain. Furthermore, the price is simply too high.
- Immutable data: Since dApps work on a decentralized model, it is impossible to make modifications in the code since everything is immutable when it comes to dApps.
- Zero scalability: dApps cannot be scaled up because of decentralization and a high level of security. Even if you try to scale up the network, the dApps get overloaded since each and every node in the network stores a huge amount of transactional data.
Bottom Line
Since security is the utmost priority in today’s times, decentralization is the future. After the introduction of decentralized cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, it is time for the apps to transform into dApps. This blog is a gentle introduction to dApps and how they function, along with a few real-life examples.
You can also explore dApps in other sectors, such as banking, eCommerce, and much more.
Recent Articles
-

Unity vs Unreal Engine 5: Which is Better?
-

Non-Negotiable Tips for Developing a P2P Lending Platform
-
The 8 Leading Cross-Platform App Development Frameworks You Should Know
-

Step-by-Step Guide: How to Build a dApp on Ethereum with Ease
-

Why Does Your Business Need Blockchain Development Company’s Expertise?

Paramjit Singh
 30th January 2024
30th January 2024